Transformational Leadership Definition
Transformational leadership is based on the ability of the leader to motivate followers through their charisma, intellectual stimulation, and individual consideration. J.M. Burns first described it in the context of political leaders as a process in which 'leaders and followers help each other to advance to a higher level of morale and motivation.'
Burns showed that the leader encourages followers to come up with new and unique ways to challenge the status quo and to alter the environment to support being successful. Such leaders enhance motivation, morale, and performance by creating a sense of identity and self to the project for followers, as well as a collective identity with the organization.
These leaders offer a role model that inspires, interests, and challenges their followers to take greater ownership for their work. A transformational leader understands the strengths and weaknesses of each follower and assigns tasks that enhance each individual's performance.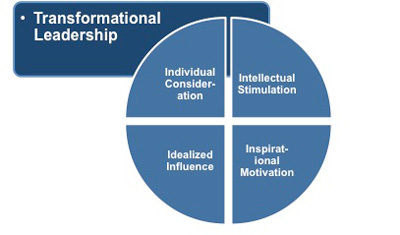 |
As a result, followers feel trust, admiration, loyalty, and respect for the leader, which means they are willing to put in whatever effort is required to achieve the goal, not just to gain benefit for themselves. There are four elements of transformational leadership:
1. Individualized Consideration - as leader you mentor your team, rewarding creativity and innovation. You actively listen to concerns and needs, offering support and empathy. You treat and challenge members according to their talents and knowledge, recognizing their contribution.
You maintain open communications and empower your members to make decisions and support them as they are implemented. This helps member self-development and their intrinsic motivation.
2. Intellectual Stimulation - your leadership encourages innovation, looks for better ways to execute tasks, and challenges previous assumptions, thereby nurturing independent thinking. You encourage new ideas without criticism and see the unexpected as a learning opportunity.
3. Inspirational Motivation - this forms the foundation of your transformational leadership in the promotion to your members of a consistent vision or mission, which is so compelling and understandable that members know what they want from every interaction. It offers them a set of values that provide a sense of meaning and challenge that is motivational. Members work enthusiastically as a team and are committed to invest considerable effort in order to attain their tasks, having a firm belief in their abilities.
4. Idealized Influence - as leader your influence is based on members seeing you as a role model they want to emulate. They view you as someone who practices what you preach. This gains members' trust and respect, as they see that your ethical conduct places their needs over your own. This shows that you and your team strive to attain organizational goals.
Transformational leadership is something that many people aspire to, and the idea of being a truly inspirational leader is very appealing. The problem is that it can be difficult to implement in a competitive and unforgiving workplace where team members are working to tight deadlines and where any mistakes would have serious consequences.
The prevailing culture of your organization and the extent to which it values the development of managerial leadership skills will affect the practical application of this leadership style.
There are two other leadership styles that you should be familiar with: Transactional Leadership and Situational Leadership.
Applied to the Team Examples
The truth is that whilst this style of leadership is the subject of countless leadership courses and seminars, its practical application is very limited. Most managers will be judged on this quarter's performance figures or whether a particular project has been delivered on time and within budget.
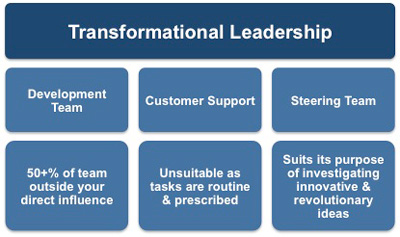 |
Development Team
As a manager of the Development Team you will be able to utilize some of the aspects of transformational leadership, but you will be limited by the fact that not all of your team come from within the IT department - 25% are seconded to you, and 38% come from outside the organization.
You may be able to assist in others achieving their personal goals but you will not be their only role model. As project manager, your performance will almost certainly be assessed in terms of the successful and timely completion of the project rather than from a staff development standpoint.
Customer Support Team
The nature of the routine and stressful work, plus the lack of opportunity for personal aspirations to be attained makes it difficult to see how this style of leadership can be incorporated into your Customer Support Team.
With virtually no promotion prospects, members see little opportunity or requirement for personal development, so adopting this style of leadership would be counterproductive for you as manager. This may seem harsh but it does reflect the reality of many low-level and poorly paid jobs.
Steering Team
As manager of the Steering Team your whole raison d'être is to investigate innovative and often revolutionary ideas, which may change the direction of the organization. For example:
• The sale of expertise to developing countries
• The setting up of a separate software company
• Breaking into new markets, e.g. insurance
• Acquisition of other utility companies
• Acquisition of suppliers, etc.
It is not difficult to imagine transformational leadership working well in the environment of a steering team as all four of the elements are both necessary and desirable if team members are to fully explore radical changes and approaches to the current business model. The majority of, if not all, members see their participation in your team as furthering their self-development and career progression. This Team Leadership Checklist reminds you of the behaviors and attitudes that you need to be a successful leader.
You may also be interested in:
Team Leadership Theories | Leadership Theories and Management | Different Leadership Styles | Transactional Leadership | Situational Leadership | Leadership Continuum.



