Goal Setting Theory Locke and Latham
Professor Edwin A Locke (born 1938) is an American psychologist and a pioneer in goal setting theory. The American Association for Psychological Science has praised him, saying,
'Locke is the most published organizational psychologist in the history of the field. His pioneering research has advanced and enriched our understanding of work motivation and job satisfaction. The theory that is synonymous with his name, goal-setting theory, is perhaps the most widely-respected theory in industrial-organizational psychology.'
Locke developed his Goal Setting Theory in 1968 in order to explain human actions in specific work situations. The theory argues that goals and intentions drive human behavior. They also are determined by our values and beliefs.
The two most important findings of this theory are that setting specific goals (e.g. I want to earn $500 more a month) generates higher levels of performance than setting vague goals (e.g. I want to earn more money). Goals that are more specific, and thus more challenging and harder to achieve, often have a direct and positive impact on performance. This relies on the notion that the harder the goal, the more a person will strive to work towards it. However, such influences on performance are mediated by two conditions:
Firstly, the goal must be accepted and acknowledged; and secondly, feedback must be used to develop areas of weakness.
Giving feedback on the strategies that are used to obtain goals is very important, especially for complex work, as challenging goals place emphasis on the final outcome rather than on performance strategies.
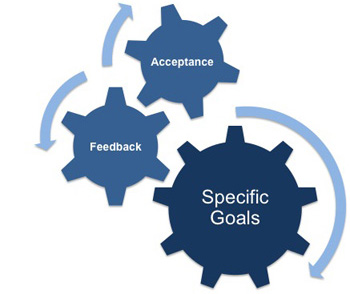 |
This allows weaknesses in performance to be overlooked which can be detrimental in the long term. Feedback is crucial to optimize results from setting goals by overcoming weaknesses as well as sustaining motivation and commitment to achieving the target.
Good feedback should:
1. Be given in a positive context.
2. Use constructive and positive language.
3. Focus on behaviors and strategies.
4. Be tailored to the needs of the individual.
5. Be a two-way communication process.
The effectiveness of goal setting may be limited if team members cannot evaluate and improve upon their performance. It is therefore vital that people are aware of their performance level and if they are on track, to allow them to progress, as well as alter their performance strategies in areas of weakness.
There are three goal-setting methods detailed in this eBook:
• 4C F - Clarity, Challenge, Complexity, Commitment & Feedback.
• SMART - Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic & Timely.
• Backward Goal Setting - work back from the end goal.
These methods complement each other. The first, '4C F,' is derived from the academic research of Dr Edwin Locke and Dr Gary Latham in the 1960s. This method encourages you to think about a goal in its widest sense and is complemented by using the second method, SMART, to then state the goal in a specific way.
Each method in isolation has both advantages and disadvantages, and so it is important to use these two methods together, as it is entirely possible that using one method on its own will produce a goal that is deficient in some way. Using both methods in tandem also gives the additional benefit that you can produce a 'goal statement' that best suits your circumstances and the culture of your organization.
For example, if a goal is set using the SMART method it may be either too complex or too simplistic. On the other hand, when using the '4C F,' a goal statement may be produced that is not as clear as one produced by the SMART method.
The third method we will discuss is known as 'Backward Goal Setting' and as the name suggests, it uses the strategy of working backwards from what you want to achieve, which makes it easier to determine the individual steps that are needed.
This method is useful where the goal is either too complex to specify in one 'goal statement' or to see how realistic your goal is within the timeframe you have. It is also useful when the goal has been set for you and you need to break it down into manageable tasks before starting.
You may also be interested in:
Goal Setting for Managers | 4CF Goal Setting | SMART Goal Setting for Managers | Backwards Goal Setting | Prioritizing Personal Goals.



