Emotional Intelligence and Management
So, what is the evidence that emotional intelligence is important in management? The work of Salovey and Mayer would almost certainly never have become known outside of academic psychology except for one key event. The year 1995 saw the publication of the bestselling book Emotional Intelligence by Dr. Daniel Goleman, followed three years later by Working with Emotional Intelligence by the same author.
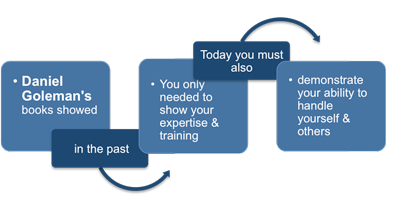 |
Both of these books were enormously influential and marked the beginning of emotional intelligence as something that was recognized by mainstream business theorists and writers.
Dr. Goleman asserted, 'The criteria for success at work are changing. We are being judged by a new yardstick: not just by how smart we are, or by our training and expertise, but also by how well we handle ourselves and each other. This yardstick is increasingly applied in choosing who will be hired and who will not, who will be let go and who retained, who passed over and who promoted…'
As we have seen, Goleman's definition of emotional intelligence proposes four broad domains of EQ. These consist of 19 competencies:
Self-Awareness
1. Emotional self-awareness: Reading one's own emotions and recognizing their impact
2. Accurate self-assessment: knowing one's strengths and limits
3. Self-confidence: a sound sense of one's self-worth and capabilities
Self-Management
4. Emotional self-control: Keeping disruptive emotions and impulses under control
5. Transparency: Displaying honesty and integrity; trustworthiness
6. Adaptability: Flexibility in adapting to changing situations or overcoming obstacles
7. Achievement: The drive to improve performance to meet inner standards of excellence
8. Initiative: Readiness to act and seize opportunities
9. Optimism: Seeing the upside in events
Social Awareness
10. Empathy: Sensing others' emotions, understanding their perspective, and taking active interest in their concerns
11. Organizational awareness: Reading the currents, decision networks, and politics at the organizational level
12. Service: Recognizing and meeting follower, client, or customer needs
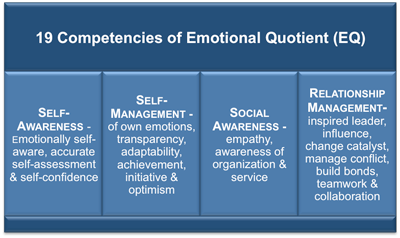 |
Relationship Management
13. Inspirational leadership: Guiding and motivating with a compelling vision
14. Influence: Wielding a range of tactics for persuasion
15. Developing others: Bolstering others' abilities through feedback and guidance
16. Change catalyst: Initiating, managing, and leading in a new direction
17. Conflict management: Resolving disagreements
18. Building bonds: Cultivating and maintaining a web of relationships
19. Teamwork and collaboration: Cooperation and team building
You may also be interested in:
Understanding Emotional Intelligence | Goleman's Model of EI | Emotional Quotient (EQ) and IQ | EQ Timeline | Can EQ be Developed? | Personal Competence | Social Competence | EQ Framework.



